Cotton is one of the most important natural fibers in the world, widely used in the textile industry. Before it reaches fabric mills, raw cotton must undergo a series of processes, one of which is baling. Baling cotton refers to compressing the cleaned and ginned cotton into dense, transportable bundles called bales. This step is critical for efficient storage, handling, and transportation. In modern agriculture and textile production, this process is largely automated through advanced Cotton Baling Machines. Let’s break down the entire baling process in detail.
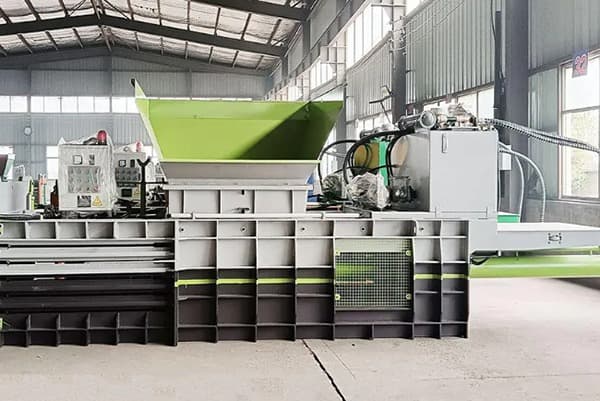

Step 1: Harvesting and Ginning
The baling process begins after the cotton is harvested from the fields. Once picked, raw cotton contains not only fibers but also seeds, dirt, and plant debris. The first step is ginning, where the cotton is cleaned and separated from seeds. The cleaned lint (fibers) then moves forward for baling. Only after the ginning process can cotton be prepared for compact packaging.
Step 2: Preparing for Compression
After cleaning, the loose cotton lint needs to be gathered and transported to the pressing section. Loose cotton takes up a lot of space and is prone to contamination. To make it more manageable, the fibers are prepared for compression. This involves fluffing and aligning the cotton fibers to ensure even distribution before being placed in a baling chamber.
Step 3: Compression with a Cotton Baling Machine
The heart of the baling process is compression, and this is where a Cotton Baling Machine plays a vital role. This machine applies hydraulic pressure to compress the loose cotton fibers into dense, uniform bales. Depending on the type of machine, pressure can range from moderate to very high, producing bales that weigh between 150 kg and 227 kg (or more) each.
Modern Cotton Baling Machines are designed for high efficiency and safety. They feature automated feeding systems, hydraulic presses, and digital controls to maintain consistent bale size and density. This automation minimizes labor costs and ensures that every bale meets industry standards for weight and dimensions.
Step 4: Wrapping and Tying the Bales
Once the cotton is compressed into a dense block, it needs to be secured. This is usually done using strong steel or polyester straps to hold the fibers tightly together. In some cases, the bales are wrapped in protective fabric or plastic covers to prevent contamination from dust, moisture, or insects during storage and transportation. Proper wrapping ensures that the quality of the cotton remains intact from the gin to the textile mill.
Step 5: Labeling and Storage
Each bale is labeled with important information such as weight, grade, and origin. Labels help mills and manufacturers identify fiber quality for specific applications. After labeling, the bales are stacked in warehouses, ready for shipment to spinning mills where the fibers will be transformed into yarn and fabric.
Importance of Using Cotton Baling Machines
The introduction of Cotton Baling Machines revolutionized the cotton industry. Before mechanization, baling was done manually or with minimal mechanical assistance, which was time-consuming and inconsistent. Modern baling machines provide:
-
Higher Efficiency – Hundreds of bales can be produced daily with minimal labor.
-
Consistent Quality – Uniform size and density make handling and transportation easier.
-
Reduced Contamination – Enclosed systems keep cotton clean during the baling process.
Conclusion
Baling cotton is a crucial step in the cotton supply chain, ensuring that the fiber can be transported and stored efficiently without compromising quality. The process involves cleaning, compressing, securing, and labeling the cotton, all of which are streamlined through advanced Cotton Baling Machines. These machines have made the process faster, safer, and more consistent, supporting the global textile industry’s demand for high-quality raw materials.
Post time: Aug-29-2025